What Is The Most Common Birth Control Pill Side Effect?

The oral contraceptive pill is a highly effective method of birth control when taken at the same time every day. When taken perfectly (no occasional forgetfulness), only 0.3% of women experience an unintended pregnancy. However, like any medication, it too may come with side effects. We recently did two polls where we asked about the most common birth control pill side effect.
Usually side effects subside during time but still, they worry people. In our polls, we wanted to dive into which ones worried most and which ones had been experienced.
The Most Common Birth Control Pill Side Effect
Almost half (45%) of the users worry about possible weight gain during pill use. If it’s of any relief, clinical studies have found no consistent association between the use of birth control pills and weight fluctuations. Usually, the weight change happens due to other reasons or is temporary.
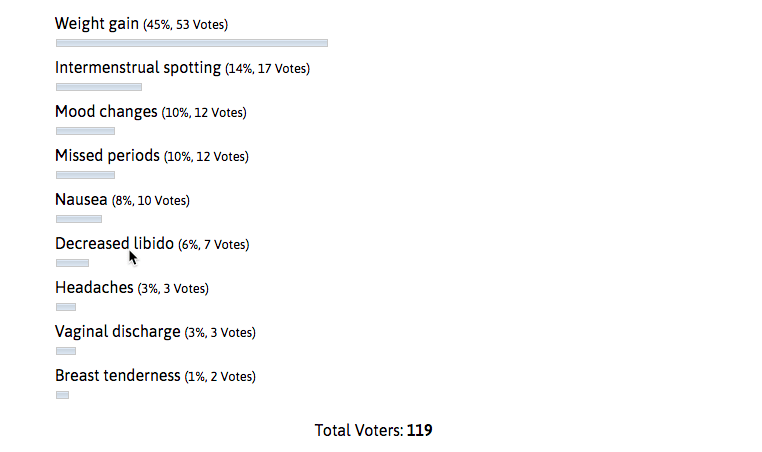
Pretty much in line with this fact is that in our other survey we noticed only 7% of users experiencing weight gain. Most common side effect experienced was actually nausea (21%). If going back to the image above, only 8% of users were worried about experiencing it. It’s good to know that these symptoms usually subside after a short time. Taking the pill with food or at bedtime can also help lower the likelihood of nausea.

(Note that for the other survey it was possible to give multiple answers, so votes do not equal 61.)
Birth Control Pill and Mood Changes
Then how about mood changes? Beforehand only 10% of people were worried about experiencing mood changes. 20% of users reported experiencing these symptoms.
This side effect has been studied a lot. For example, a 2015 study of 90 women published in Human Mapping found that use of the birth control pills was associated with smaller cortical thickness measurements in the lateral orbitofrontal cortex and the posterior cingulate cortex. Now that’s a mouthful…
What does it mean? These areas of the brain are linked with reward response and evaluating incoming stimuli, and it means that the pill could be messing with how you feel about things.
No need to sound the panic alarm though. Authors mention further research needs to be conducted to confirm whether or not there is a connection between cortical thinning in these areas of the brain, mood changes, and birth control pill use. In any case, anyone experiencing mood changes during pill use should contact their medical provider.
When Should You Contact a Doctor?
It is important that anyone who experiences any of the following side effects while taking the pill contacts their medical provider or visits an emergency room immediately, as they may signify a serious condition.
Birth control pill side effects that should be investigated are:
- A: Abdominal/stomach pain
- C: Chest pain (as well as shortness of breath)
- H: Headaches that are severe
- E: Eye problems such as blurred vision or loss of vision
- S: Swelling or aching in the legs and thighs (also redness, swelling or pain in the calf or thighs).
These symptoms can be remembered using the acronym ACHES.
Related articles
References:
- Association of Reproductive Health Professionals, Health matters fact sheet, accessed 20 August 2015.
- Brown University, Birth control pills (BCPs), accessed 27 February 2015.
- Oral contraceptive pill use is associated with localized decreases in cortical thickness, Nicole Petersen et al., Human Brain Mapping, doi: 10.1002/hbm.22797, published online 2 April 2015, abstract.



